Documentation Errors, how to avoid them in Pharma and Lab
“Documentation is terrible” is a deep reflective thought of people around the world but the question arises “Why is it painful to read so much documentation?” It is probably considered as a boring task with the least creativity and fun and is frequently a time-sink. It is somehow like a monster in the corner, an elephant in the room, and the darkness to assert your job. In this article, we will take a look at the challenges in laboratory documentation, and explore how to mitigate documentation errors by implementing good documentation practices in Labs and Pharmaceutical Industry.
As far as the pharmaceutical industry is concerned, it is inundated with words and documents in different forms. Documentation is the lifeblood of all quality systems. “The activity isn’t done until the completion of paperwork” is a famous saying told to all employees in the pharmaceutical world from the very beginning. If documentation sucks, why keep doing it anyway? As Documentation is a crucial part of any system, its importance cannot be disregarded. Wietse Venema, a dutch scientist illustrates its importance with his brilliant words “Lack of documentation is a problem for acceptance”. Now it is readily apparent that documentation cannot be brushed aside. Rather than daunting the pessimism of documentation one should find ways to cope with it.

Why is documentation obligatory for laboratories and pharmaceutical industries?
Documentation is an indispensable element to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) compliance. It certifies traceability of all manufacturing, development, and testing activities in laboratories and pharmaceutical industries. It is an excellent tool that controls the course of action which is ultimately directed towards quality control. As a matter of fact, without standard documentation practice, any pharmaceutical industry has no vindication to unveil products to market. There is no other practice or element other than documentation practice that has a greater influence on the bottom line of the pharmaceutical industry and scientific laboratory.
Standard Laboratory Document Types
The standard types of documents kept by any industry or laboratory are listed below:
Quality manual
A quality manual is a document that outlines an organization’s quality management system (QMS). It typically includes an overview of the QMS, the organization’s quality policy, quality objectives, and the roles and responsibilities of those involved in implementing and maintaining the system. The quality manual is an important document for demonstrating an organization’s commitment to quality to external stakeholders, such as customers and regulatory agencies.
Policies
Policies are documents that outline an organization’s rules, guidelines, and procedures. They can cover a wide range of topics, from human resources policies such as vacation and sick leave, to environmental policies that address waste disposal and energy consumption. Policies provide a framework for decision-making and ensure that everyone within an organization is aware of the expectations and standards that are in place.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
A standard operating procedure (SOP) is a step-by-step guide that outlines how to perform a particular task or process. SOPs are used to ensure that processes are consistent and repeatable, and they help to minimize errors and reduce variability in results. SOPs are commonly used in laboratory and industrial settings to ensure that processes are performed consistently and to a high standard.
Batch records
Batch records are documents that provide a detailed record of the production process for a particular batch of a product. They typically include information on the raw materials used, the processing steps performed, and the testing and quality control measures applied. Batch records are important for ensuring that products are produced consistently and to a high standard, and they are often required by regulatory agencies.
Test methods
Test methods are documents that describe how to perform a particular test or analysis. They provide instructions on how to prepare samples, perform the test, and interpret the results. Test methods are used in laboratory settings to ensure that testing is performed consistently and to a high standard, and they are often required by regulatory agencies.
Specifications
Specifications are documents that outline the requirements for a particular product or material. They typically include information on the physical, chemical, and performance characteristics that the product must meet. Specifications are important for ensuring that products are produced consistently and to a high standard, and they are often required by regulatory agencies.
Logbooks
Logbooks are documents that provide a record of events or activities. They are commonly used in laboratory and industrial settings to record data, observations, and actions. Logbooks are important for ensuring that activities are documented accurately and that there is a clear record of what has been done. They can also be used for troubleshooting, trend analysis, and quality control purposes.

The Documentation Challenge in Labs and Pharmaceutical Industry
To regulate current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP), appropriate documentation and records must be properly maintained by a pharmaceutical manufacturer. Humans are prone to errors, so there is a great chance of any inaccuracy while paper documentation practices. To subjugate this problem, most laboratories and pharmaceutical companies are switching towards digitalization. Digital or electronic documentation has made the documentation process free of human errors.
In the past, numerous tragic incidents were reported, merely caused by incorrect documentation practice. The inaccurate written status of a single drug led to the taking lives of five persons in 1972 in Davenport, UK. The drug products were reported to be sterile but they were contaminated by which people caught infections. This was due to an unwritten modification to the operation of an autoclave, which was orally communicated between operators, and came about with dextrose intravenous solutions that were contaminated. By this incident, sterility assurance was introduced operationally. Moreover, the requirements and processes of equipment validation were developed, and the agency was explicitly given all the legal rights of the inspection.
How to overcome the risk of documentation errors?
Documentation errors can have serious consequences in pharmaceutical industries and scientific laboratories. All pharmaceutical industries and scientific laboratories must undergo some useful practices to avoid the risk of these documentation errors. By establishing the following hierarchical document system, pharmaceuticals industries and laboratories can prevent the catastrophic risks of documentation errors.
Hierarchical document system to avoid risks of documentation errors
The following hierarchical document system can be established to prevent the catastrophic risks of documentation errors:
Level 1 – Quality manual:
The quality manual is the top-level document that outlines an organization’s quality management system (QMS) and provides an overview of the company’s policies and procedures. It sets the tone for the entire organization and establishes the company’s commitment to quality. By ensuring that the quality manual is up-to-date, accurate, and reflective of the organization’s practices, companies can prevent errors from occurring.
Level 2 – Company policies:
Company policies are documents that outline an organization’s rules, guidelines, and procedures. They provide a framework for decision-making and ensure that everyone within an organization is aware of the expectations and standards that are in place. By ensuring that policies are clearly written, up-to-date, and accessible to all employees, companies can prevent errors from occurring.
Level 3 – Standard operating procedures (SOPs):
SOPs are step-by-step guides that outline how to perform a particular task or process. They provide instructions for consistency and repeatability, and help minimize errors and reduce variability in results. By ensuring that SOPs are clear, concise, and followed consistently, companies can prevent errors from occurring.
Level 4 – Batch records, specifications, test methods, and validation documents:
These documents provide specific details related to product development, testing, and release. By ensuring that these documents are accurate, up-to-date, and reflective of the company’s practices, companies can prevent errors from occurring.
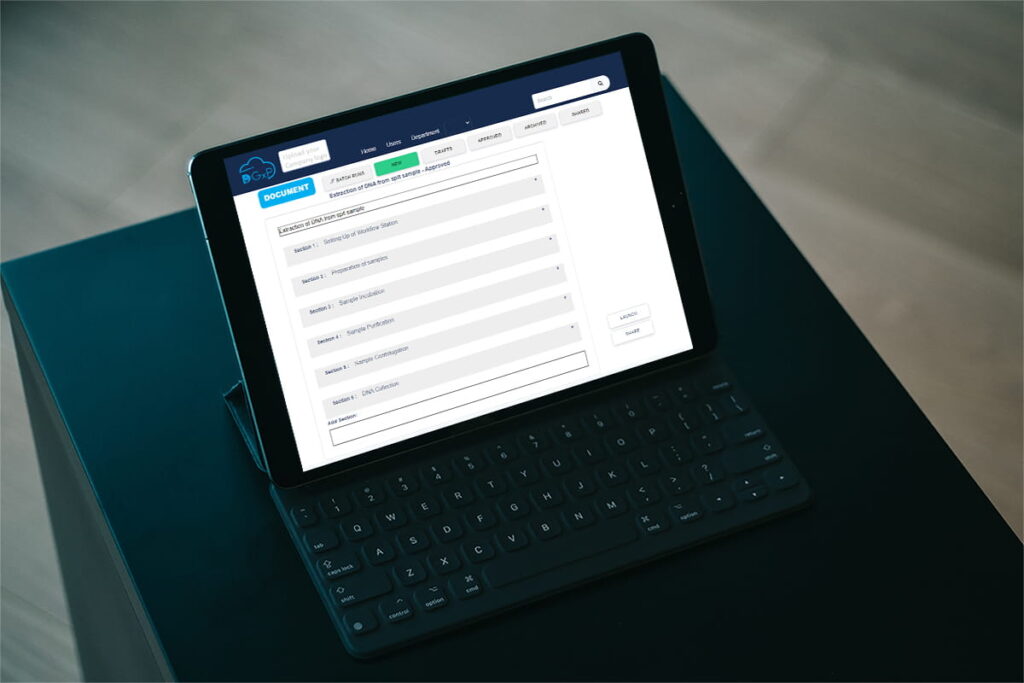
Good Documentation Practices to overcome the risks of documentation errors
To overcome the risk of documentation errors, in addition to establishing a hierarchical document system, there are several other practices that can be implemented. These practices include:
Regular training on documentation practices:
Companies can provide regular training to their employees on documentation practices, including how to write, review, and approve documents. This training can also cover document retention policies and the importance of accurate documentation. By providing regular training, companies can ensure that all employees are aware of the best practices for creating and maintaining accurate documentation.
Implementing document version control:
Document version control is the process of managing changes to documents over time. By implementing a system of version control, companies can ensure that only the most up-to-date version of a document is being used. This can help to prevent errors that can occur when different versions of a document are used simultaneously.
Performing regular document reviews and audits:
Regular document reviews and audits can help to identify potential errors in documentation. These reviews can be conducted by internal or external auditors, and can help to ensure that documents are accurate, up-to-date, and in compliance with regulatory requirements. By performing regular reviews and audits, companies can catch errors early and take corrective action.
Overall, these practices can help to ensure that documentation errors are caught and corrected before they become a problem. By implementing a combination of a hierarchical document system, regular training on documentation practices, document version control, and regular document reviews and audits, pharmaceutical industries and scientific laboratories can reduce the risk of documentation errors and ensure that accurate documentation is maintained.

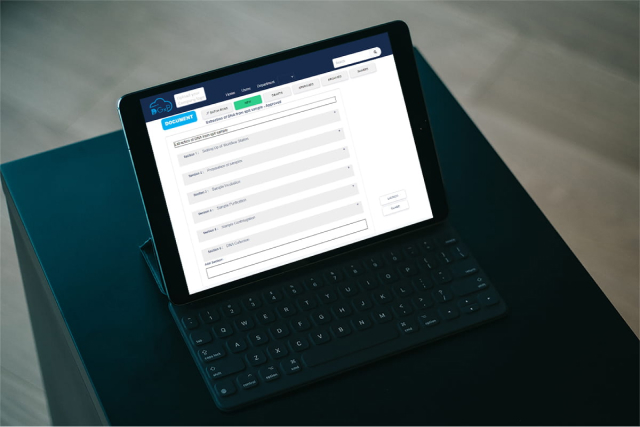
Implement Digital Documentation to eliminate documentation errors
In order to fully comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory requirements, proper documentation and record-keeping are essential. Without proper documentation, there is no way to trace the manufacturing, development, and testing activities of a laboratory or pharmaceutical industry. This can lead to serious consequences, such as product recalls, loss of reputation, and even legal action.
However, traditional paper-based documentation practices are prone to human errors and can be time-consuming, which can result in mistakes or omissions. This is why many laboratories and pharmaceutical companies are switching to digital or electronic documentation, which can eliminate errors and make the documentation process more efficient.
Digital documentation offers several advantages. It is easily accessible, searchable, and can be stored securely on servers, reducing the risk of document loss or theft. Digital documentation can also be updated easily and quickly, ensuring that the latest information is always available to the users. Moreover, electronic signatures and timestamps can provide an added layer of security and ensure authenticity.

Digital GxP is a digital documentation software specifically designed for pharmaceutical laboratories. It offers several features that can streamline documentation practices and make the process more efficient. Digital SOPs and video SOPs, for instance, can provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform specific tasks or procedures, reducing the likelihood of errors and ensuring consistency across the board. Electronic batch records and laboratory information management systems (LIMS) can provide a comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to the final product, making it easier to identify any deviations or issues.
By implementing Digital GxP, laboratories and pharmaceutical companies can not only comply with cGMP but also ensure that their documentation practices are efficient, accurate, and secure. This can help to reduce the risk of errors, improve quality control, and ultimately lead to better products and outcomes for patients.
So, if you’re looking to streamline your documentation practices and take advantage of the benefits of digital documentation, sign up for Digital GxP today!